Technology in the service of diabetes patients
Improving the quality of life, managing the disease and avoiding complications
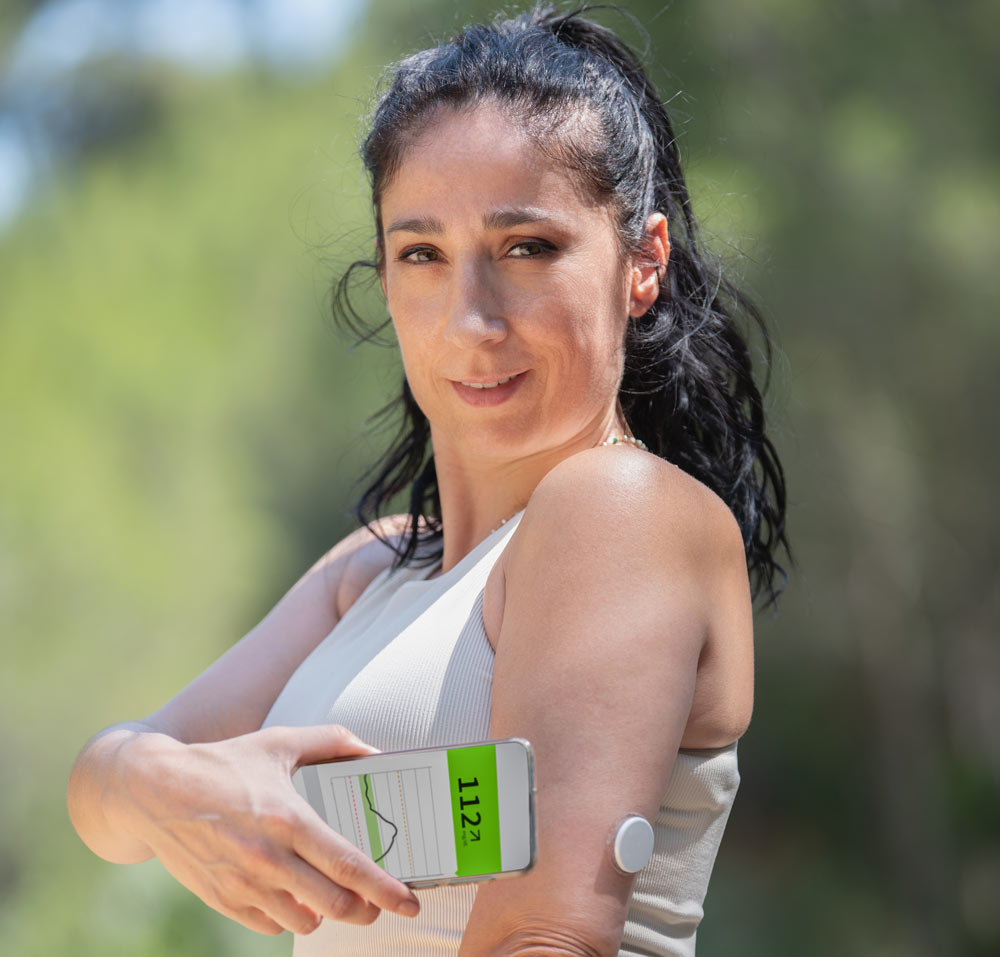

Modern technology has helped provide safety for diabetes patients by alerting them when their blood sugar levels are imbalanced. This allows them to administer the appropriate insulin dose at the right time with extreme precision. International companies have put great emphasis on developing and producing devices that monitor blood sugar levels, are easy to use, are accurate at the same time to manage diabetes and warn patients of any changes without the need for finger pricking.
In light of technological advancements in all medical fields, companies have been able to develop tiny devices that monitor blood sugar levels throughout the day. Doctors focus on keeping blood sugar levels within normal ranges for as long as possible to avoid complications.
The importance of technology for diabetes patients lies in achieving better control over sugar levels, and reducing the occurrence of disease complications, which was not possible in the past. Additionally, technology has a positive impact on improving the quality of life for diabetes patients.
Thanks to advanced devices, diabetes patients can improve their quality of life, engage in daily activities, and increase the effectiveness of managing their condition.
Some benefits of using technology for diabetes patients include:
- Helping patients control blood sugar levels.
- Avoiding complications of the disease.
- Flexible disease management.
- Improving patient quality of life.
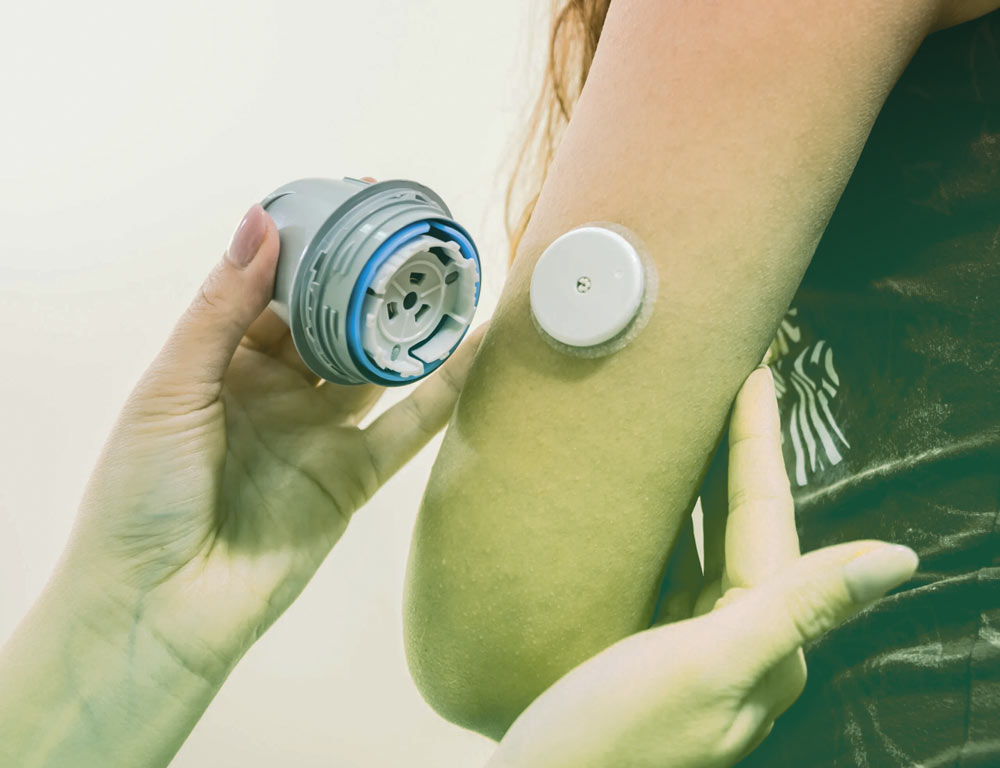
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Devices
A small sensor placed under the skin allows blood sugar levels to be seen through a smartphone, suitable for all ages. Thus, it can be said that modern technology has contributed to defeating diabetes and controlling it by predicting its increase or decrease with the help of continuous glucose monitoring devices.
These are highly accurate medical devices and technologies that protect diabetes patients and enable them to control and monitor their blood sugar levels 24/7. If blood sugar levels rise or fall, the device gives an immediate alert signal to the person so they can deal with their health situation promptly.
With these devices, patients can plan appropriate meals and balance their diet and physical activity to avoid sudden drops or spikes in blood sugar and sense any changes in their glucose levels before they occur, allowing for quick response and treatment.
As a result, patients are protected from the severe complications resulting from changes in blood sugar levels, which can affect all body parts. These devices contribute to improving the quality of life of diabetes patients through smart alerts and remote monitoring technology.
Studies have shown the role and importance of these devices in regulating both types of blood sugar, as they provide better control over blood sugar regularity through continuous monitoring of sugar readings and the ability to show changes in sugar levels throughout the day and night.
The basic standards relied upon by continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices are the percentage of blood sugar level readings throughout the day to determine whether it is low, high, or within a reasonable range. Experts have agreed that “time in range” is one of the measures for assessing the effectiveness of diabetes management, as it provides more actionable information than the A1C test alone. This measure can be read as a percentage that includes the average hours and minutes for each blood sugar level per day, depending on the patient’s circumstances.
As for the importance of this technology for doctors, they have observed in recent years the importance of patients being fully aware not only of their current blood sugar readings but also their previous readings throughout the day, as well as the expected readings in the next minutes or hours. This helps doctors make more informed decisions and tailor their treatment plans to patients’ needs.
Scientifically proven and from the experiences of diabetic patients and healthcare practitioners, there is a significant improvement in sugar levels alongside the patients’ ability to manage diabetes with regular use of these technologies.
Insulin Pump
A small electronic device consists of an insulin reservoir and a thin plastic tube connected to a small needle that is inserted under the skin. The device continuously pumps insulin into the human body and is programmed by the treating physician to deliver the required amount of insulin the patient needs. The pumping rate also depends on the number of daily carbohydrates and sugars the patient consumes.
Insulin pumps are very suitable for diabetic patients, especially children, according to studies in this regard, which have confirmed an improvement in their quality of life compared to their peers who follow traditional methods in treating diabetes. Insulin pumps have also helped control blood sugar levels better, reduce the risk of hypoglycemia, especially at night, and assist in lowering cumulative blood sugar levels and preventing or delaying diabetes complications.
One of the advantages of the insulin pump is its ability to be pre-programmed and provide insulin as needed, which reduces cases of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, and over time helps reduce cumulative blood sugar levels. The pump also features accuracy in regulating blood sugar levels, providing the body with only what it needs. Thus, the patient has greater freedom in eating. It is also the latest means of continuously and regularly delivering insulin throughout the day, providing the patient with stability in blood sugar levels and allowing him to lead an everyday life and cope flexibly.
The developments in medical technology have contributed to the invention of this alternative therapeutic solution, significantly reducing the risk of hypoglycemia while eliminating the need for patients to inject themselves throughout the day. It also provides a more remarkable ability to control blood sugar levels.
According to studies, using insulin pumps reduces severe blood sugar spikes or hypoglycemia episodes. In explaining how it works, the pump continuously delivers insulin to the body 24 hours a day in programmed doses by the treating physician, mimicking how the pancreas delivers typically insulin in a healthy person.
When a drop in blood sugar level below the acceptable level is observed, the pump automatically and temporarily stops delivering insulin for a period of up to two hours, which prevents the patient from the risk of severe hypoglycemia and its associated complications.
On the other hand, when the patient consumes their meal and the amount of carbohydrates is entered, the pump delivers insulin proportional to the amount of carbohydrates, and this is called mealtime bolus delivery.